How To Create An Excel Sheetmusic Database Template
Abstract: This is the start tutorial in a series designed to get you acquainted and comfy using Excel and its built-in data mash-up and analysis features. These tutorials build and refine an Excel workbook from scratch, build a data model, so create astonishing interactive reports using Power View. The tutorials are designed to demonstrate Microsoft Business Intelligence features and capabilities in Excel, PivotTables, Power Pivot, and Power View.
Note:This article describes information models in Excel 2013. Yet, the same data modeling and Power Pivot features introduced in Excel 2013 also employ to Excel 2016.
In these tutorials you larn how to import and explore information in Excel, build and refine a information model using Ability Pin, and create interactive reports with Power View that you tin publish, protect, and share.
The tutorials in this series are the following:
-
Import Information into Excel 2013, and Create a Data Model
-
Extend Data Model relationships using Excel, Power Pin, and DAX
-
Create Map-based Power View Reports
-
Incorporate Cyberspace Data, and Set up Power View Report Defaults
-
Power Pin Help
-
Create Amazing Power View Reports - Part two
In this tutorial, you lot start with a blank Excel workbook.
The sections in this tutorial are the following:
-
Import data from a database
-
Import information from a spreadsheet
-
Import data using copy and paste
-
Create a relationship betwixt imported information
-
Checkpoint and Quiz
At the end of this tutorial is a quiz you can accept to exam your learning.
This tutorial series uses data describing Olympic Medals, hosting countries, and diverse Olympic sporting events. Nosotros suggest you go through each tutorial in lodge. Also, tutorials use Excel 2013 with Power Pivot enabled. For more information on Excel 2013, click here. For guidance on enabling Ability Pivot, click here.
Import data from a database
We commencement this tutorial with a blank workbook. The goal in this department is to connect to an external information source, and import that data into Excel for farther analysis.
Let's kickoff past downloading some data from the Internet. The data describes Olympic Medals, and is a Microsoft Access database.
-
Click the following links to download files we use during this tutorial series. Download each of the four files to a location that'due south easily accessible, such as Downloads or My Documents, or to a new folder you create:
> OlympicMedals.accdb Access database
> OlympicSports.xlsx Excel workbook
> Population.xlsx Excel workbook
> DiscImage_table.xlsx Excel workbook -
In Excel 2013, open a blank workbook.
-
Click DATA > Get External Data > From Access. The ribbon adjusts dynamically based on the width of your workbook, so the commands on your ribbon may look slightly different from the following screens. The first screen shows the ribbon when a workbook is broad, the second image shows a workbook that has been resized to accept up only a portion of the screen.
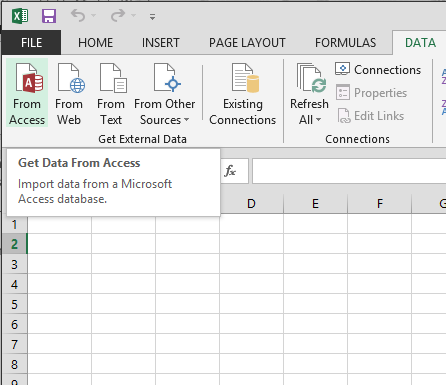
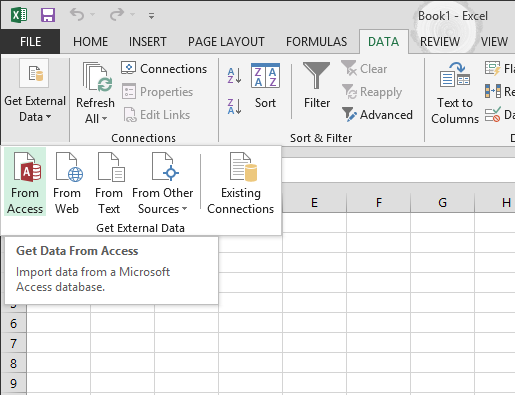
-
Select the OlympicMedals.accdb file you downloaded and click Open. The following Select Table window appears, displaying the tables found in the database. Tables in a database are similar to worksheets or tables in Excel. Cheque the Enable pick of multiple tables box, and select all the tables. And so click OK.
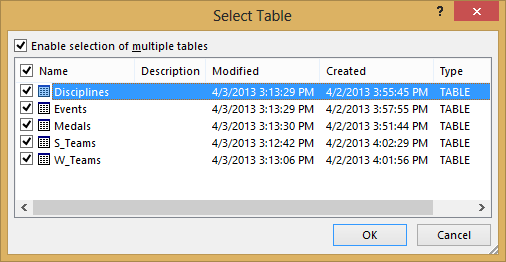
-
The Import Data window appears.
Annotation:Notice the checkbox at the lesser of the window that allows yous to Add this data to the Information Model, shown in the post-obit screen. A Data Model is created automatically when you import or work with two or more tables simultaneously. A Data Model integrates the tables, enabling extensive analysis using PivotTables, Power Pin, and Ability View. When you import tables from a database, the existing database relationships between those tables is used to create the Data Model in Excel. The Data Model is transparent in Excel, but you can view and change information technology directly using the Power Pivot add together-in. The Information Model is discussed in more detail afterward in this tutorial.
Select the PivotTable Written report option, which imports the tables into Excel and prepares a PivotTable for analyzing the imported tables, and click OK.
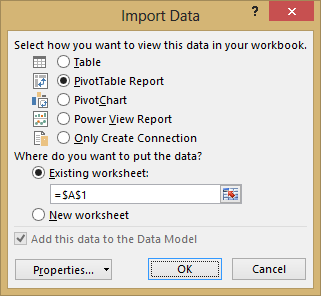
-
Once the information is imported, a PivotTable is created using the imported tables.
With the data imported into Excel, and the Data Model automatically created, you lot're ready to explore the data.
Explore information using a PivotTable
Exploring imported data is like shooting fish in a barrel using a PivotTable. In a PivotTable, you elevate fields (similar to columns in Excel) from tables (similar the tables you but imported from the Access database) into different areas of the PivotTable to adjust how it presents your data. A PivotTable has four areas: FILTERS, COLUMNS, ROWS, and VALUES.
It might take some experimenting to decide which area a field should be dragged to. You tin can drag as many or few fields from your tables as you like, until the PivotTable presents your information how you desire to run into it. Feel gratis to explore by dragging fields into different areas of the PivotTable; the underlying data is non affected when you lot accommodate fields in a PivotTable.
Let's explore the Olympic Medals information in the PivotTable, starting with Olympic medalists organized past discipline, medal type, and the athlete's state or region.
-
In PivotTable Fields, expand the Medals tabular array past clicking the arrow beside it. Observe the NOC_CountryRegion field in the expanded Medals table, and drag it to the COLUMNS area. NOC stands for National Olympic Committees, which is the organizational unit for a land or region.
-
Adjacent, from the Disciplines tabular array, drag Discipline to the ROWS area.
-
Let'southward filter Disciplines to display only five sports: Archery, Diving, Fencing, Effigy Skating, and Speed Skating. You can do this from inside the PivotTable Fields surface area, or from the Row Labels filter in the PivotTable itself.
-
Click anywhere in the PivotTable to ensure the Excel PivotTable is selected. In the PivotTable Fields list, where the Disciplines table is expanded, hover over its Discipline field and a dropdown arrow appears to the right of the field. Click the dropdown, click (Select All)to remove all selections, and then ringlet downwards and select Archery, Diving, Fencing, Figure Skating, and Speed Skating. Click OK.
-
Or, in the Row Labels section of the PivotTable, click the dropdown next to Row Labels in the PivotTable, click (Select All) to remove all selections, so coil down and select Archery, Diving, Fencing, Figure Skating, and Speed Skating. Click OK.
-
-
In PivotTable Fields, from the Medals table, drag Medal to the VALUES area. Since Values must be numeric, Excel automatically changes Medal to Count of Medal.
-
From the Medals tabular array, select Medal again and drag it into the FILTERS area.
-
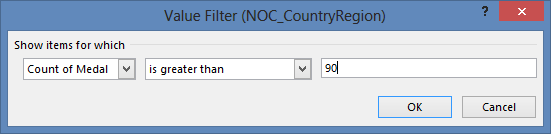
Let'due south filter the PivotTable to display only those countries or regions with more than xc total medals. Here's how.
-
In the PivotTable, click the dropdown to the right of Column Labels.
-
Select Value Filters and select Greater Than….
-
Blazon 90 in the concluding field (on the right). Click OK.
-
Your PivotTable looks like the following screen.
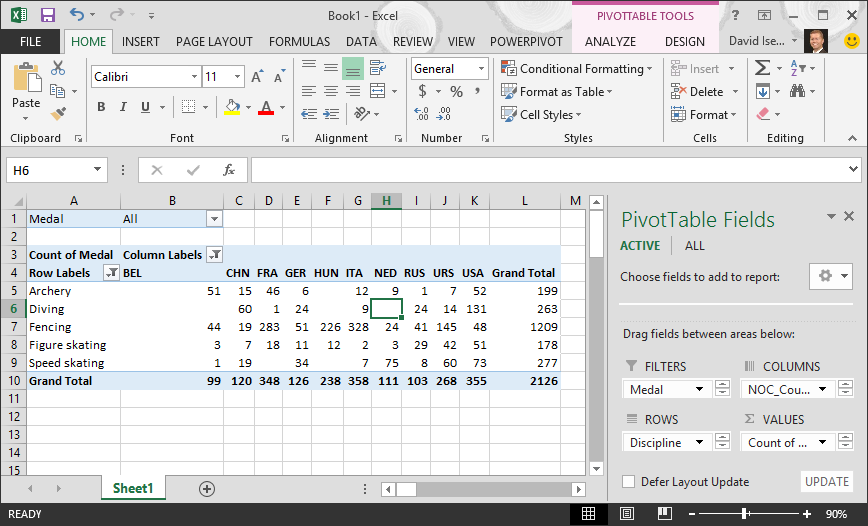
With little effort, you now have a basic PivotTable that includes fields from three dissimilar tables. What fabricated this task then elementary were the pre-existing relationships amid the tables. Considering table relationships existed in the source database, and because you imported all the tables in a unmarried operation, Excel could recreate those table relationships in its Information Model.
But what if your data originates from different sources, or is imported at a later on time? Typically, y'all can create relationships with new data based on matching columns. In the adjacent step, you lot import additional tables, and acquire how to create new relationships.
Import information from a spreadsheet
At present let's import data from some other source, this time from an existing workbook, then specify the relationships between our existing data and the new data. Relationships permit yous clarify collections of information in Excel, and create interesting and immersive visualizations from the data yous import.
Let's outset past creating a blank worksheet, then import data from an Excel workbook.
-
Insert a new Excel worksheet, and name it Sports.
-
Browse to the folder that contains the downloaded sample information files, and open OlympicSports.xlsx.
-
Select and re-create the data in Sheet1. If you select a cell with data, such equally prison cell A1, you can printing Ctrl + A to select all adjacent information. Close the OlympicSports.xlsx workbook.
-
On the Sports worksheet, identify your cursor in prison cell A1 and paste the data.
-
With the data still highlighted, printing Ctrl + T to format the data as a table. You can also format the information equally a table from the ribbon by selecting HOME > Format every bit Tabular array. Since the data has headers, select My table has headers in the Create Table window that appears, equally shown here.
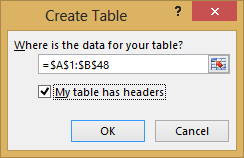
Formatting the data as a table has many advantages. You tin can assign a name to a table, which makes information technology like shooting fish in a barrel to identify. Yous tin can likewise plant relationships between tables, enabling exploration and assay in PivotTables, Power Pivot, and Power View.
-
Name the tabular array. In Tabular array TOOLS > Pattern > Properties, locate the Table Name field and type Sports. The workbook looks like the following screen.
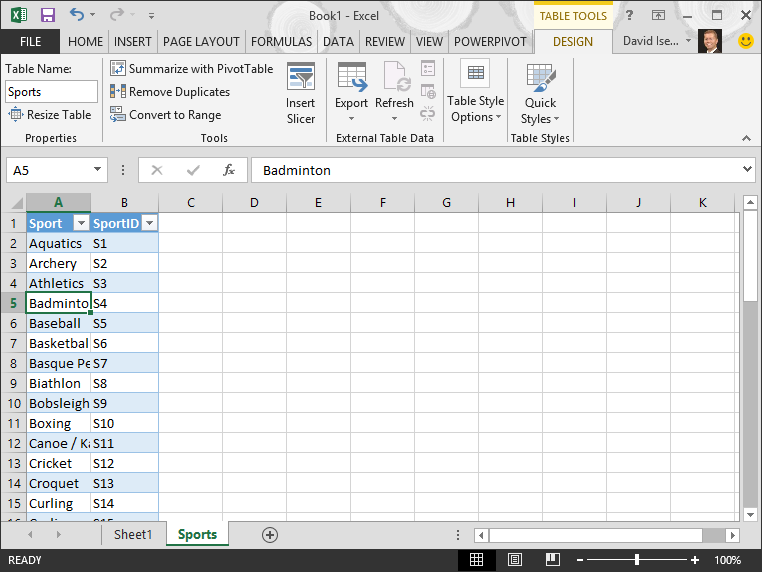
-
Salve the workbook.
Import information using re-create and paste
Now that nosotros've imported data from an Excel workbook, allow'southward import data from a table we find on a web page, or whatsoever other source from which we can copy and paste into Excel. In the following steps, you add the Olympic host cities from a table.
-
Insert a new Excel worksheet, and name it Hosts.
-
Select and re-create the following table, including the table headers.
| Urban center | NOC_CountryRegion | Alpha-2 Code | Edition | Season |
| Melbourne / Stockholm | AUS | AS | 1956 | Summer |
| Sydney | AUS | AS | 2000 | Summer |
| Innsbruck | AUT | AT | 1964 | Winter |
| Innsbruck | AUT | AT | 1976 | Winter |
| Antwerp | BEL | BE | 1920 | Summer |
| Antwerp | BEL | Exist | 1920 | Winter |
| Montreal | Tin can | CA | 1976 | Summer |
| Lake Placid | Tin | CA | 1980 | Winter |
| Calgary | CAN | CA | 1988 | Wintertime |
| St. Moritz | SUI | SZ | 1928 | Winter |
| St. Moritz | SUI | SZ | 1948 | Wintertime |
| Beijing | CHN | CH | 2008 | Summertime |
| Berlin | GER | GM | 1936 | Summer |
| Garmisch-Partenkirchen | GER | GM | 1936 | Winter |
| Barcelona | ESP | SP | 1992 | Summer |
| Helsinki | FIN | FI | 1952 | Summer |
| Paris | FRA | FR | 1900 | Summer |
| Paris | FRA | FR | 1924 | Summer |
| Chamonix | FRA | FR | 1924 | Winter |
| Grenoble | FRA | FR | 1968 | Winter |
| Albertville | FRA | FR | 1992 | Winter |
| London | GBR | UK | 1908 | Summer |
| London | GBR | U.k. | 1908 | Wintertime |
| London | GBR | United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland | 1948 | Summer |
| Munich | GER | DE | 1972 | Summer |
| Athens | GRC | GR | 2004 | Summer |
| Cortina d'Ampezzo | ITA | IT | 1956 | Wintertime |
| Rome | ITA | IT | 1960 | Summer |
| Turin | ITA | Information technology | 2006 | Wintertime |
| Tokyo | JPN | JA | 1964 | Summer |
| Sapporo | JPN | JA | 1972 | Winter |
| Nagano | JPN | JA | 1998 | Winter |
| Seoul | KOR | KS | 1988 | Summer |
| United mexican states | MEX | MX | 1968 | Summertime |
| Amsterdam | NED | NL | 1928 | Summer |
| Oslo | NOR | NO | 1952 | Winter |
| Lillehammer | NOR | NO | 1994 | Winter |
| Stockholm | SWE | SW | 1912 | Summer |
| St Louis | The states | Us | 1904 | Summer |
| Los Angeles | USA | US | 1932 | Summer |
| Lake Placid | U.s. | US | 1932 | Winter |
| Squaw Valley | USA | U.s. | 1960 | Wintertime |
| Moscow | URS | RU | 1980 | Summer |
| Los Angeles | USA | U.s. | 1984 | Summer |
| Atlanta | United states | US | 1996 | Summertime |
| Salt Lake City | USA | U.s. | 2002 | Winter |
| Sarajevo | YUG | YU | 1984 | Wintertime |
-
In Excel, place your cursor in cell A1 of the Hosts worksheet and paste the information.
-
Format the data as a tabular array. As described earlier in this tutorial, yous printing Ctrl + T to format the information as a table, or from HOME > Format equally Tabular array. Since the data has headers, select My tabular array has headers in the Create Table window that appears.
-
Name the table. In Tabular array TOOLS > DESIGN > Backdrop locate the Table Name field, and type Hosts.
-
Select the Edition column, and from the Dwelling house tab, format it equally Number with 0 decimal places.
-
Salvage the workbook. Your workbook looks like the post-obit screen.
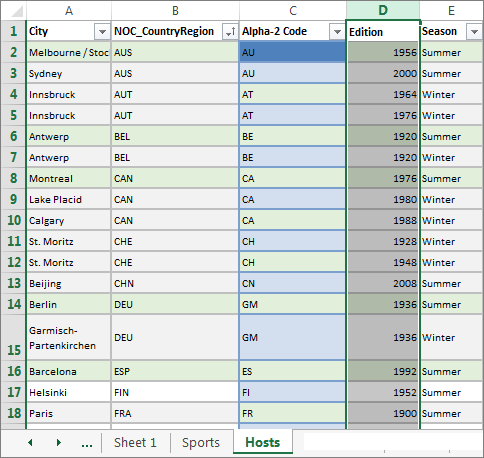
Now that you have an Excel workbook with tables, yous can create relationships betwixt them. Creating relationships between tables lets you lot mash upward the data from the 2 tables.
Create a relationship between imported data
You tin can immediately begin using fields in your PivotTable from the imported tables. If Excel tin can't determine how to incorporate a field into the PivotTable, a relationship must be established with the existing Data Model. In the following steps, you learn how to create a relationship between data you imported from different sources.
-
On Sheet1, at the peak ofPivotTable Fields, clickAll to view the complete list of available tables, as shown in the following screen.
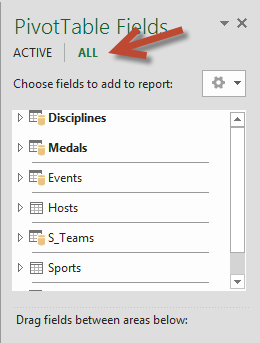
-
Curl through the list to encounter the new tables you lot just added.
-
Expand Sports and select Sport to add it to the PivotTable. Discover that Excel prompts you to create a relationship, as seen in the following screen.
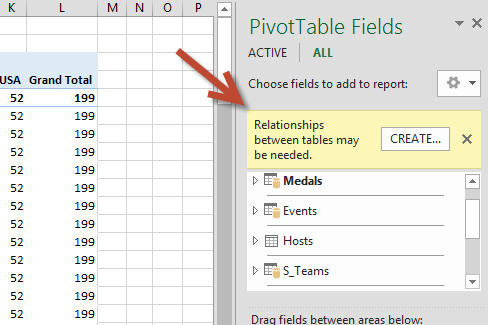
This notification occurs because you used fields from a table that's not part of the underlying Data Model. One way to add a table to the Information Model is to create a relationship to a table that's already in the Data Model. To create the relationship, one of the tables must have a cavalcade of unique, non-repeated, values. In the sample data, the Disciplines tabular array imported from the database contains a field with sports codes, chosen SportID. Those same sports codes are present every bit a field in the Excel data we imported. Allow'southward create the relationship.
-
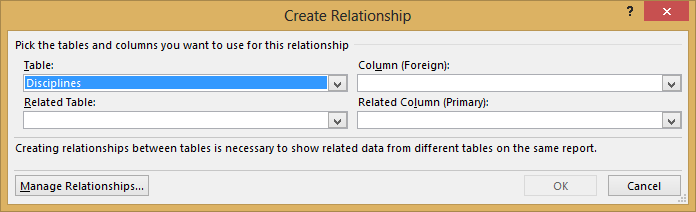
Click CREATE... in the highlighted PivotTable Fields area to open the Create Human relationship dialog, equally shown in the post-obit screen.
-
In Table, choose Disciplines from the drop downwardly list.
-
In Column (Strange), choose SportID.
-
In Related Tabular array, cull Sports.
-
In Related Cavalcade (Primary), choose SportID.
-
Click OK.
The PivotTable changes to reflect the new human relationship. But the PivotTable doesn't look right quite yet, because of the ordering of fields in the ROWS surface area. Discipline is a subcategory of a given sport, just since nosotros bundled Subject to a higher place Sport in the ROWS area, it's not organized properly. The post-obit screen shows this unwanted ordering.
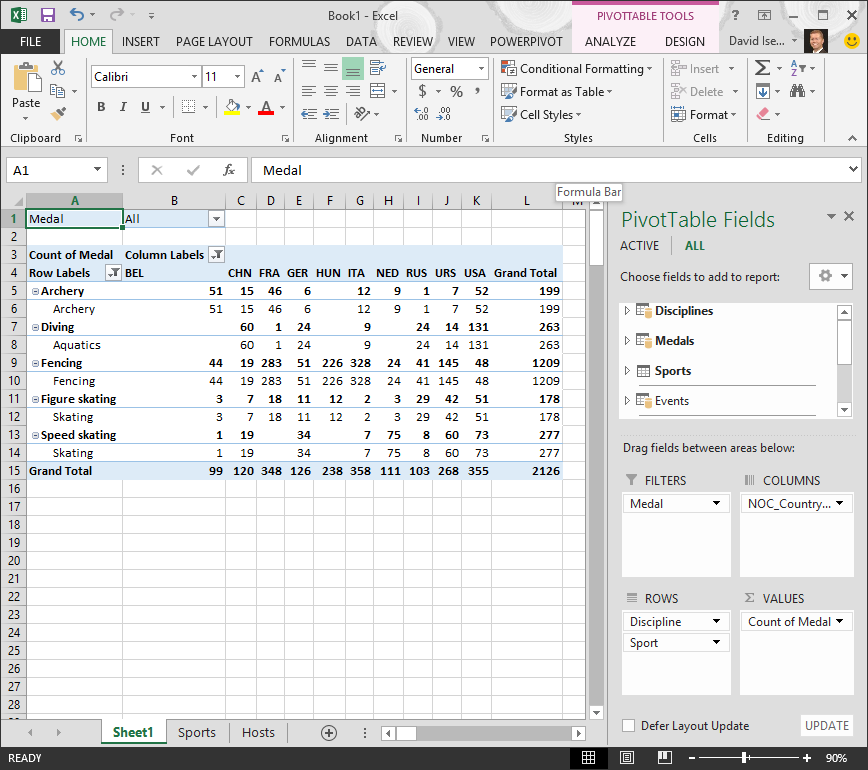
-
In the ROWS surface area, movement Sport above Discipline. That's much better, and the PivotTable displays the data how you want to see it, as shown in the following screen.
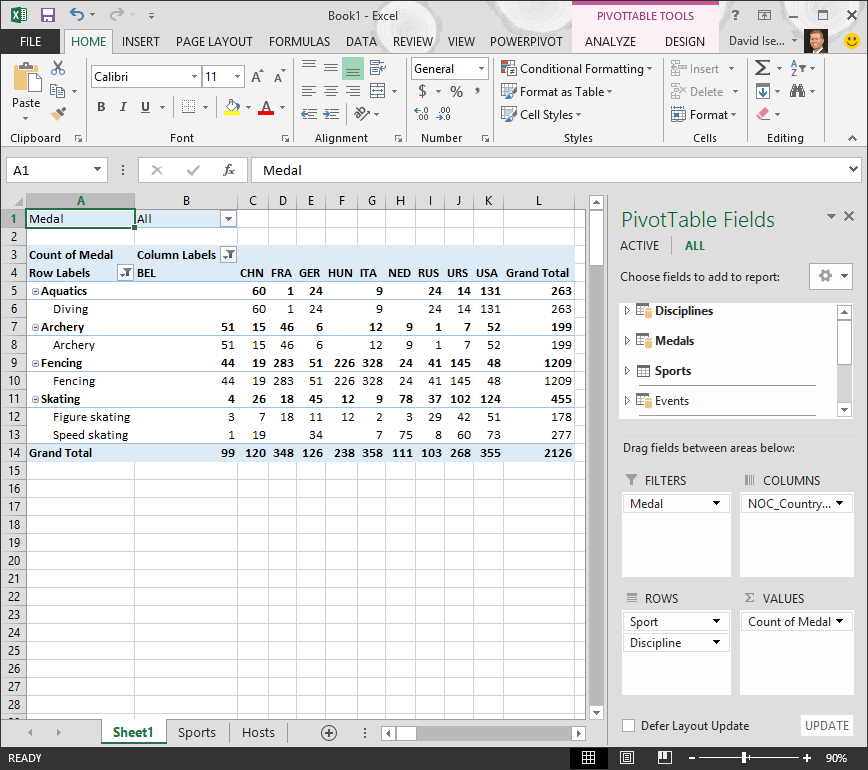
Behind the scenes, Excel is building a Information Model that tin can be used throughout the workbook, in any PivotTable, PivotChart, in Power Pin, or whatsoever Power View report. Table relationships are the basis of a Data Model, and what determine navigation and adding paths.
In the next tutorial, Extend Information Model relationships using Excel 2013, Power Pivot, and DAX, you build on what you learned hither, and step through extending the Data Model using a powerful and visual Excel add-in chosen Power Pivot. You also learn how to calculate columns in a tabular array, and use that calculated column so that an otherwise unrelated table can be added to your Data Model.
Checkpoint and Quiz
Review What Yous've Learned
You lot now accept an Excel workbook that includes a PivotTable accessing information in multiple tables, several of which you imported separately. Y'all learned to import from a database, from another Excel workbook, and from copying information and pasting it into Excel.
To make the data piece of work together, you had to create a table relationship that Excel used to correlate the rows. You also learned that having columns in one table that correlate to data in some other table is essential for creating relationships, and for looking up related rows.
You're ready for the adjacent tutorial in this series. Here's a link:
Extend Data Model relationships using Excel 2013, Power Pin, and DAX
QUIZ
Want to run into how well you call back what yous learned? Here's your chance. The following quiz highlights features, capabilities, or requirements you learned about in this tutorial. At the lesser of the folio, y'all'll notice the answers. Good luck!
Question 1: Why is it of import to convert imported data into tables?
A: You don't accept to convert them into tables, because all imported data is automatically turned into tables.
B: If you catechumen imported information into tables, they volition be excluded from the Data Model. Only when they're excluded from the Information Model are they available in PivotTables, Power Pivot, and Ability View.
C: If you convert imported information into tables, they can be included in the Data Model, and exist made bachelor to PivotTables, Power Pin, and Power View.
D: You cannot convert imported data into tables.
Question ii: Which of the following data sources tin can y'all import into Excel, and include in the Data Model?
A: Access Databases, and many other databases also.
B: Existing Excel files.
C: Annihilation you can re-create and paste into Excel and format as a table, including data tables in websites, documents, or anything else that can be pasted into Excel.
D: All of the above
Question 3: In a PivotTable, what happens when you reorder fields in the iv PivotTable Fields areas?
A: Nothing – y'all cannot reorder fields one time you place them in the PivotTable Fields areas.
B: The PivotTable format is changed to reflect the layout, merely underlying data is unaffected.
C: The PivotTable format is changed to reverberate the layout, and all underlying information is permanently inverse.
D: The underlying data is changed, resulting in new data sets.
Question four: When creating a relationship between tables, what is required?
A: Neither tabular array tin accept any column that contains unique, non-repeated values.
B: One table must not be part of the Excel workbook.
C: The columns must not be converted to tables.
D: None of the above is correct.
Quiz Answers
-
Right answer: C
-
Correct reply: D
-
Correct answer: B
-
Correct respond: D
Notes:Information and images in this tutorial series are based on the post-obit:
-
Olympics Dataset from Guardian News & Media Ltd.
-
Flag images from CIA Factbook (cia.gov)
-
Population data from The World Banking company (worldbank.org)
-
Olympic Sport Pictograms by Thadius856 and Parutakupiu
How To Create An Excel Sheetmusic Database Template,
Source: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/tutorial-import-data-into-excel-and-create-a-data-model-4b4e5ab4-60ee-465e-8195-09ebba060bf0
Posted by: hulingslithend.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Create An Excel Sheetmusic Database Template"
Post a Comment